Additive manufacturing: a dynamic and innovative industry
Since the invention of the first 3D printing technologies in the early 1980s, the 3D printing market has seen an enormous amount of innovation and interest. A niche technology until key patents expired, the 2010s saw the emergence of many start-ups offering inexpensive consumer 3D printers.
The ensuing media frenzy in the early 2010s thrust 3D printing into the limelight, accompanied by large multinational corporations like HP and GE entering the 3D printing space. After years of hype, the industry has shifted to a more critical examination of the added value that additive manufacturing brings to businesses and supply chains. Despite the hurdles posed by the COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing supply chain disruptions, the additive manufacturing market continues to find new applications and new end users.
IDTechEx predicts that continued innovation and significant adoption of 3D printing will drive the hardware and consumables market to exceed $41 billion by 2033.
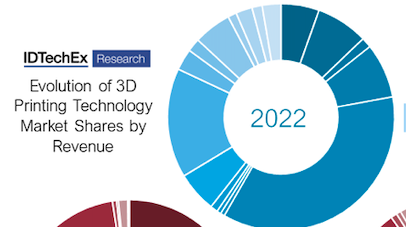
IDTechEx has studied the 3D printing industry for over a decade and has released its latest report providing the most comprehensive view of the market. Looking at thirty individual 3D printing technologies and five broad material categories, IDTechEx finds a continuing theme between these important aspects of the industry: expansion.
Developing thanks to new technologies, the actors
Since established additive manufacturing technologies such as selective laser sintering and thermoplastic filament extrusion date back decades, the market can be expected to consolidate and stabilize from a technological standpoint. . However, new entrants with their own unique innovations on 3D printing appear every year, some of which are so unique that they do not fit into the classic framework of the seven printing processes. New technologies, which cover polymers, metals, electronics, ceramics, construction and composite 3D printing, offer different advantages and disadvantages to incumbents. Along with these new technologies, more incremental improvements are being made to established processes. What both advancements enable is access to new applications and new end users that 3D printing previously struggled to reach.
3D printing ecosystem: materials, software, post-processing, services
Along with the expansion and improvement of the 3D printing hardware portfolio, the growth of the broader 3D printing ecosystem includes materials, post-processing, software and services. For example, the portfolio of 3D printing materials is growing due to the arrival on the market of the aforementioned new technologies, which can process materials previously underutilized or underutilized by additive manufacturing. Additionally, the software, scanners and 3D printing services industry is introducing new offerings to simplify the adoption of additive manufacturing by end users, making their experience more seamless.
————————
Click on here for more information on this report.

Comments are closed.